In 2017, I decided to depart from my homeland, Nepal, and pursue further academic achievements in the United States. After graduation, international students tend to face difficulties in finding employment due to visa requirements, but those who overcome these challenges can get well-paying jobs that can improve their living standards significantly.
However, international students who are interested in investing may hesitate due to visa uncertainties and the long-term commitment that investing requires. Despite this, I believe investing is still important for international students, especially through retirement plans offered by employers, as it provides an opportunity to learn about financial markets and can benefit future career and personal finance management.
The Importance of Investing: A Common Scenario
To illustrate the significance of investing, I will give an example that is very common among international students, including some of my friends. Many of them do not utilize their 401(k) plans provided by their employers during the early stage of their careers until their immigration status is more stable.
The typical reason they give is that they are unsure if they will still be in the country when they can withdraw their funds without penalties. While this reason might seem valid, let’s do a simple calculation to see if it is better to participate in the 401(k) plan or not.
A Simple Calculation: 401(k) vs. No Contribution
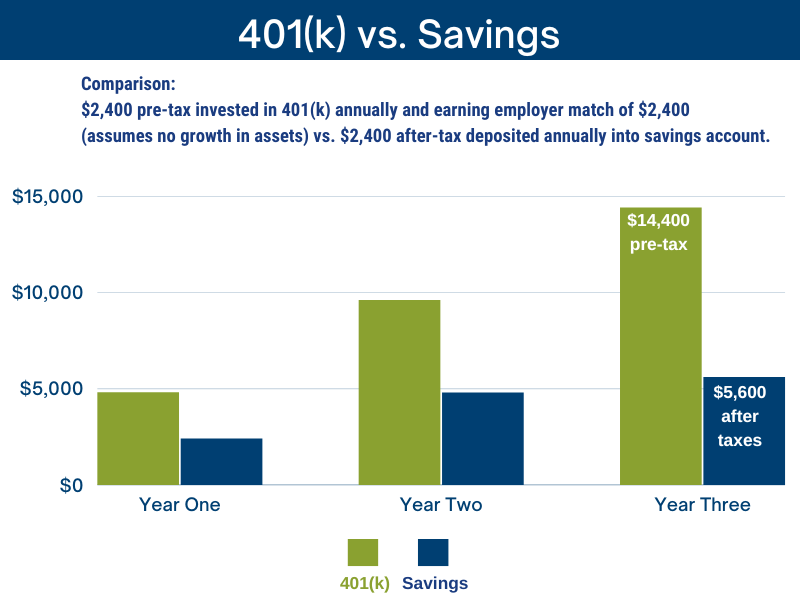
Suppose your income is $80,000, and your employer matches 100% of your contributions up to 3%. If you contribute 3% of your income to your 401(k) plan, you will contribute $2,400 per year (Pre-Tax). With the employer’s matching contribution, the total annual contribution to the 401(k) plan will be $4,800 (Pre-Tax).
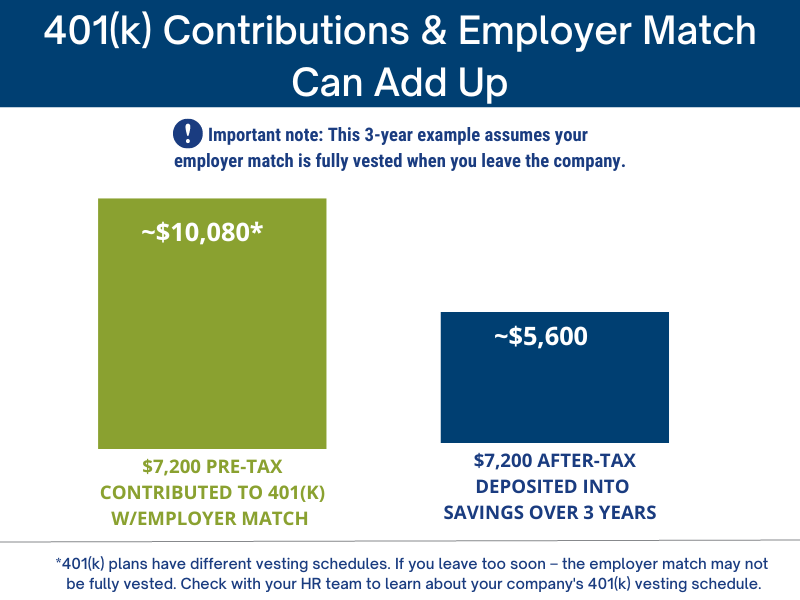
Now, let’s assume you have to leave the country after three years. The total contribution made by that time would be $14,400. If you assume no growth in the investments, the total amount in your 401(k) plan after three years will be $14,400, with $7,200 contributed by you and $7,200 contributed by your employer, both pre-tax. If you didn’t contribute, and the $7,200 were deposited directly into your bank account, you would receive only $5,600 after taxes.
Taxation and Penalties: It Adds Up
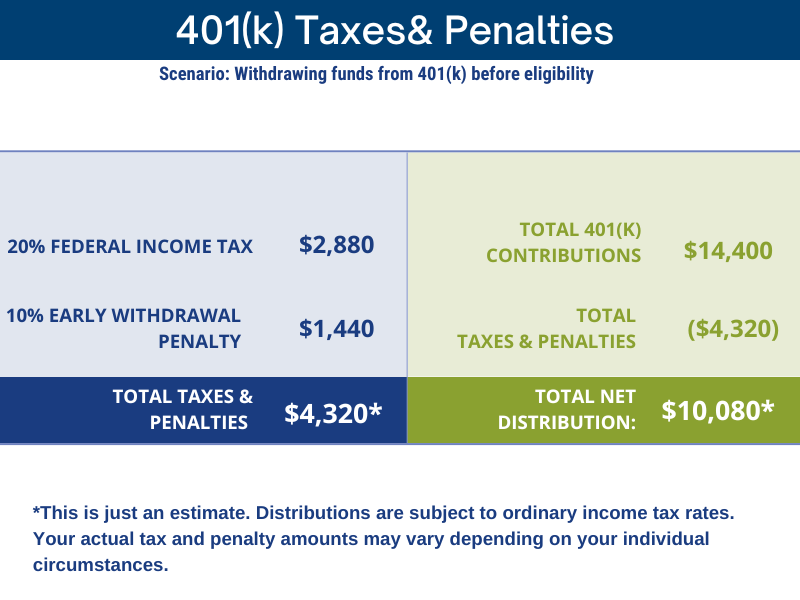
If you left the country and withdrew $14,400 from your 401(k) before retirement age, you would be subject to taxes and penalties. Assuming a federal tax rate of 20%, you would owe $2,880 in federal income taxes. You may also owe state income taxes, depending on where you live. Moreover, you will also have to pay a penalty of 10% of the amount withdrawn, which in this case is $1,440.
In total, the amount you would have to pay to the IRS for withdrawing $14,400 from your 401(k) before retirement age would be $4,320, which is a significant amount. (It is important to note that this is just an estimate, and your actual tax and penalty amounts may vary depending on your individual circumstances. Your 401(k) distributions are subject to ordinary income tax rates. This means the more you make – the more they take.)
Benefits of Investing
In the end, your $7,200 pre-tax contributions made over three years will result in roughly $10,000 in your bank as compared to the $5,600 if you did not contribute to your 401(k). Contributing to a 401(k) to receive your employer match typically outweighs the taxes and penalties associated with taking the funds out early. It may be unpleasant to pay a 10% penalty, but it is worthwhile because the possibility of a 50%-100% rate of return obtained through the “free lunch” of the employer match is significant.
Your contributions to the 401(k) are always 100% vested, the employer match may not be. In the example above, we assume that the employer match is 100% vested at the time the employee leaves. Many 401(k)s have vesting schedules[1], if you leave your employer too soon, the employer match may not be fully vested. You will need to talk with your (or read the 401(k) Summary Plan description) to learn the specifics about your 401(k) plan.
The Value of Experience: Learning and Setting Up Future Success
Another important aspect to consider is the invaluable experience you will gain through managing money, saving for retirement, and learning from investment mistakes. This experience is certainly worth more than the dollar amount earned during that period.
People in their 20s should see this time as an opportunity to accelerate their learning because the long-term returns on that knowledge outweigh the simple dollar calculation of what is earned. Although the future might not be certain for international students in the US, investing can help them learn about personal financial management and set themselves up for future success.
[1] https://www.irs.gov/retirement-plans/plan-participant-employee/retirement-topics-vesting